
Moulding
The following page of notes will cover:
- Blow moulding
- Injection moulding
- Vacuum forming
- Extrusion
- Rotational moulding
Blow moulding:
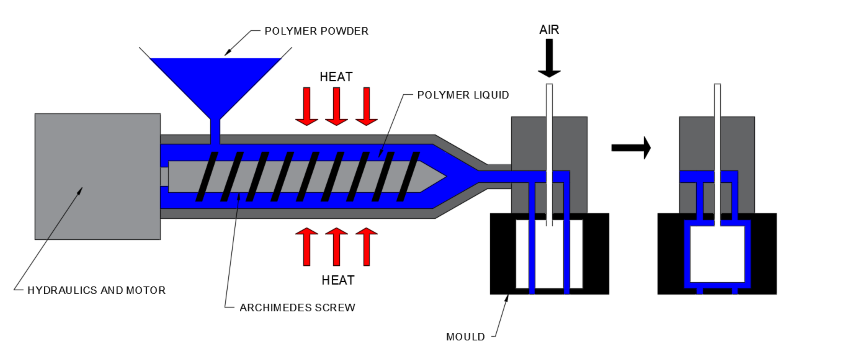
How it works:
- Plastic granules fed through hopper
- Heated/melted along the Archimedes screw
- Extruded into hollow tube (parison)
- Tube is then clamped into metal mould
- Air is pumped in to inflate mould
- Mould/bottle is cooled to solidify plastic
- Product is ejected and trimmed
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Plastic bottles, containers
Injection moulding:
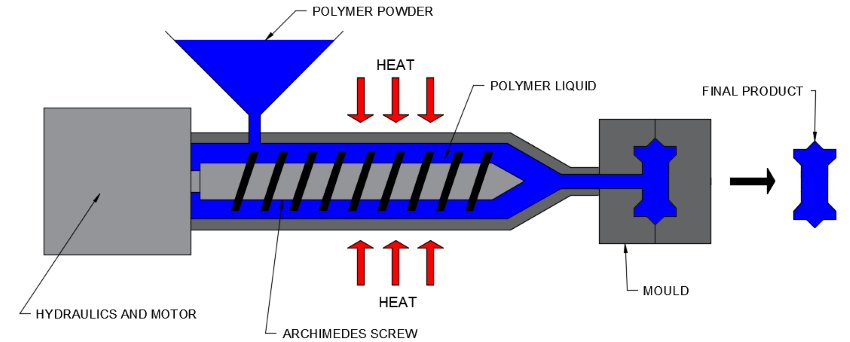
How it works:
- Plastic granules fed through hopper
- Heated/melted along the Archimedes screw
- Plastic injected into the mould
- Two-part mould "negative" of the product
- Product rapidly cooled and ejected from mould
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Casings for electric products, containers for storage/packaging
Vacuum forming:
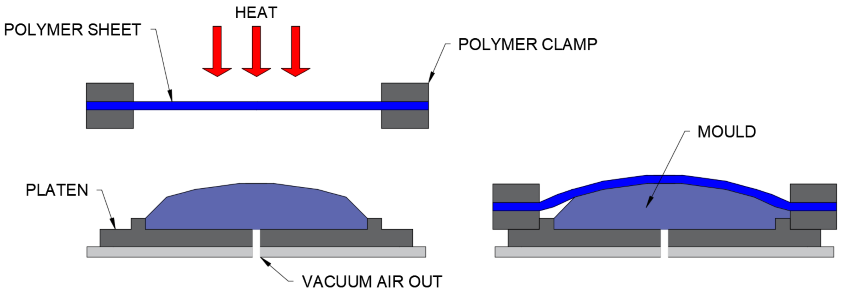
How it works:
- Create mould (air gaps, tapers, angles, rounded egdges)
- Place the mould on the platen and lower
- Clamps HIPS and heat until 'bouncy'
- Raise platen into plastic
- Vacuum pump air out
- Blowback a little bit of air to help release mould
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Yoghurt pots, blister packaging, inside of fridges
Extrusion:
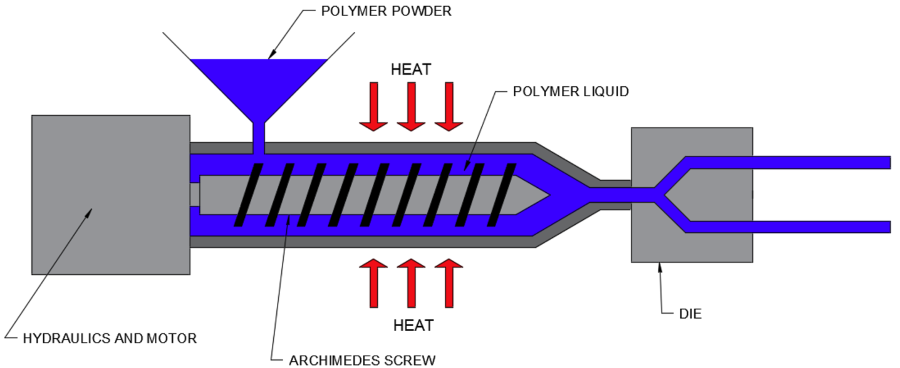
How it works:
- Plastic granules fed through hopper
- Heated/melted along the Archimedes screw
- Plastic forced into the die
- The plastic is extruded 'pulled' throug the die and cooled
- Rollers pull plastic continuously
- The extruded product is cut to the desired lengths
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
Uses: Collapsible tubes, guttering, straws, gear blanks
Rotational moulding:
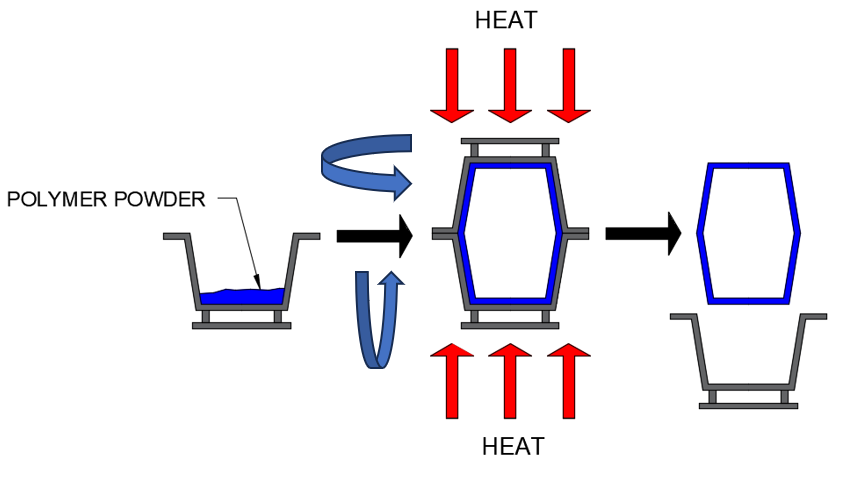
How it works:
- Powdered polymer loaded into mould
- Heat is applied to the mould
- At the same time the mould is rotated on all 3 axis (x, y, z)
- After some time, the mould is cooled and the component is removed
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|